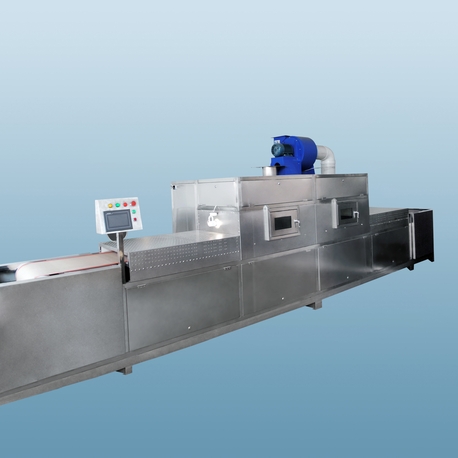
In today's fast-paced industrial food processing and manufacturing sectors, efficiency and quality are paramount. The process of thawing frozen materials, a critical step in countless production lines, has evolved dramatically from traditional time-consuming methods. At the heart of this revolution is microwave defrost technology. This article delves into the world of industrial microwave thawing, exploring the technology behind it, the benefits of continuous systems, how to choose a reliable industrial microwave defroster manufacturer, and addresses common challenges faced by operators.

The Science Behind Industrial Microwave Defrost
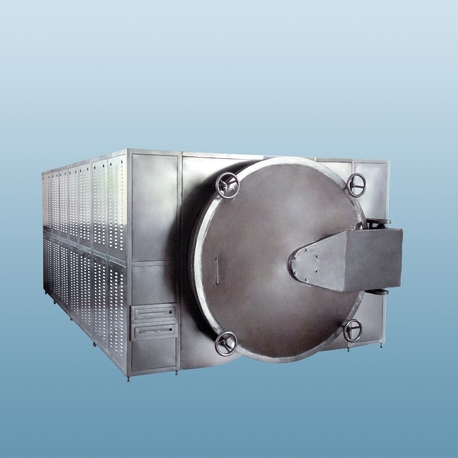
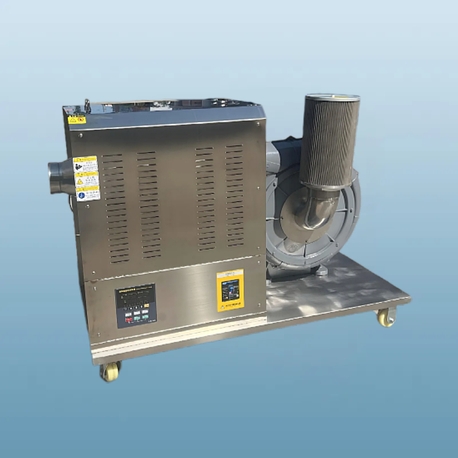
An industrial microwave defroster operates on the same fundamental principle as a domestic microwave oven, but scaled up with immense power and sophisticated control systems. Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic energy that cause polar molecules, most notably water, to oscillate billions of times per second. This movement generates heat from within the product itself.
Unlike conventional methods like air or water thawing that work from the outside in, microwave energy penetrates the product and provides rapid, volumetric heating. This means the entire mass of a frozen block—whether it's meat, fruit, vegetables, or dairy—begins to warm up simultaneously. This core-to-surface heating process is what allows an industrial microwave defroster to achieve thawing times that are a fraction of those required by traditional methods, turning a process that once took 24-48 hours into one that takes mere minutes.
Why Choose a Continuous Microwave Defroster?
For high-volume processing plants, batch-type thawing can become a bottleneck. This is where the continuous microwave defroster becomes a game-changer. This system is designed as an integrated conveyor belt line where frozen products enter at one end and uniformly thawed products exit at the other, ready for the next processing stage.
The advantages of a continuous system are profound:
Uninterrupted Production: It enables a constant, seamless flow of material, aligning perfectly with modern continuous processing lines and eliminating downtime between batches.
Remarkable Consistency: Advanced sensors and software continuously monitor and adjust the microwave power in real-time based on the product's load, size, and initial temperature. This ensures every piece, from the beginning to the end of a production run, is thawed to the exact same specified temperature.
Maximized Space Efficiency: These systems have a much smaller footprint compared to large holding rooms or water baths required for batch thawing equivalent volumes.
Enhanced Quality Control: The precise and rapid nature of microwave defrost minimizes the "drip loss"—the loss of valuable proteins and nutrients in thawed meat and fish—and drastically reduces the risk of bacterial growth that occurs when food sits in the "temperature danger zone" (40°F - 140°F) for prolonged periods.
Selecting the Right Industrial Microwave Defroster Manufacturer
Investing in an industrial microwave defroster is a significant decision. The manufacturer you choose will directly impact the technology's performance, reliability, and your return on investment. Here are key factors to consider when selecting an industrial microwave defroster manufacturer:
Industry Experience and Reputation: Look for a manufacturer with a proven track record and extensive experience in your specific industry, whether it's meat, poultry, seafood, fruit, or prepared foods. Ask for case studies and client references.
Technical Expertise and Support: The best manufacturers don't just sell equipment; they become partners. Evaluate their ability to provide comprehensive technical support, from initial process consultation and installation to training, maintenance, and readily available spare parts.
Customization Capabilities: No two production lines are identical. A top-tier manufacturer will offer custom-engineered solutions tailored to your specific product type, throughput requirements, and existing factory layout.
Focus on Safety and Compliance: Ensure the equipment is designed and built to meet all relevant international safety standards (e.g., IEC, UL) for industrial microwave equipment to protect operators and ensure compliance.
Testing and Validation: A reputable manufacturer will always offer to test your actual product in their facility. This process validates the thawing parameters and guarantees the system will perform as expected in your plant.

Common Challenges and Problems in Microwave Defrosting
While highly effective, microwave thawing is a precise science. Understanding common challenges is the first step to mitigating them.
Uneven Thawing (Runaway Heating): This is the most frequently cited issue. It occurs when thawed parts of the product (which absorb microwave energy more efficiently than frozen parts) become hotter, leading to localized cooking while other areas remain frozen. This is often due to:
Inconsistent Product Size/Shape: A system calibrated for a uniform fillet will struggle with a random mix of sizes.
Incorrect Power Configuration: Power must be carefully matched to the product type and volume.
Solution: Modern industrial systems use techniques like mode stirrers, controlled power pulsing, and sophisticated software algorithms to distribute energy more evenly. Proper product preparation and system calibration are crucial.
Partial Cooking: If the energy input is too high or the residence time too long, the edges of protein-based products can begin to cook, altering texture and appearance.
Solution: Precise temperature control and using a "tempering" approach—thawing to just below 0°C (32°F) where the product is still firm but not frozen—allows for easy processing without cooking.
Arcing (Spark Discharge): Metal contaminants (e.g., a stray piece of foil or a metal clip) within the product can cause sparks inside the microwave cavity, which can damage the equipment and be a fire hazard.
Solution: Implementing rigorous metal detection protocols upstream of the microwave defrost unit is essential. Modern systems are also built with arc detection sensors that can shut down the magnetrons instantly if arcing is detected.
System Maintenance: Industrial magnetrons have a finite lifespan and are the most expensive component to replace. Waveguides and stirrers can also require maintenance.
Solution: Partnering with a manufacturer that offers a clear preventive maintenance schedule and readily available parts is critical. Training your maintenance team on basic upkeep can prevent major downtime.
High Initial Investment: The upfront cost of an industrial microwave system can be higher than that of a traditional thawing room.
Solution: Frame the purchase as a long-term investment. The ROI is realized through drastically reduced energy costs (compared to refrigerated air systems), lower labor costs, minimized product loss, increased throughput, and superior end-product quality.
The Future of Industrial Thawing
The adoption of microwave defrost technology is a clear indicator of the industry's shift towards smarter, faster, and more sustainable processing. As technology advances, we can expect even greater integration with IoT (Internet of Things) for predictive maintenance and real-time data analytics, further optimizing the thawing process and providing unprecedented traceability for quality assurance.
For any operation looking to modernize its production line, improve product quality, and boost efficiency, exploring the capabilities of an industrial microwave defroster is a logical and profitable step. By carefully selecting an experienced industrial microwave defroster manufacturer and understanding how to leverage a continuous microwave defroster, businesses can truly revolutionize their thawing process.es, or hardware failure in the PLC.
Solution: Regularly back up cycle recipes and data. Use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to protect the control system from power fluctuations. Keep software firmware updated as recommended by the manufacturer.
Regular preventive maintenance, proper operator training, and a strong partnership with your equipment supplier are the best defenses against these common issues, ensuring your freeze dryer machine operates reliably for years to come.