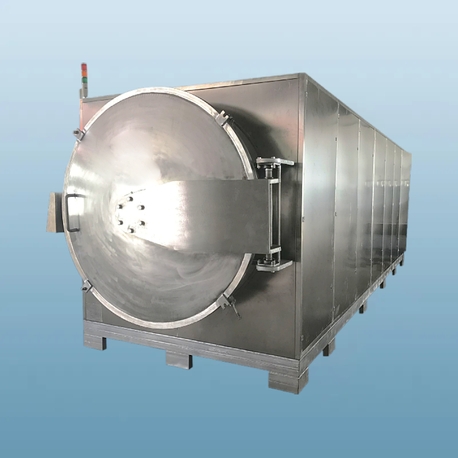
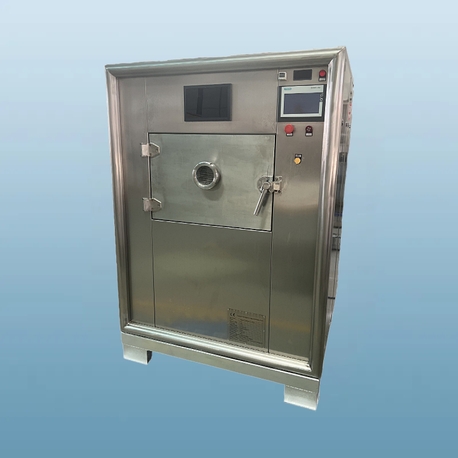
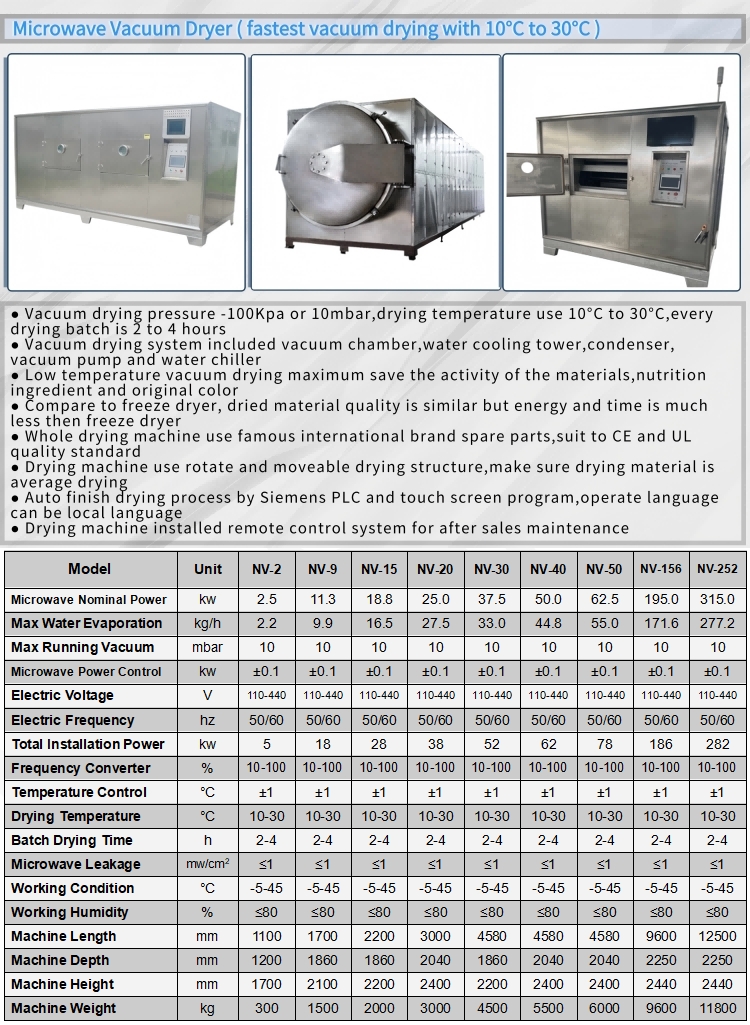
- Vacuum Microwave Dryer
- Microwave Dryer
- Microwave Sterilizer
- Hot Air + Microwave Dryer
-
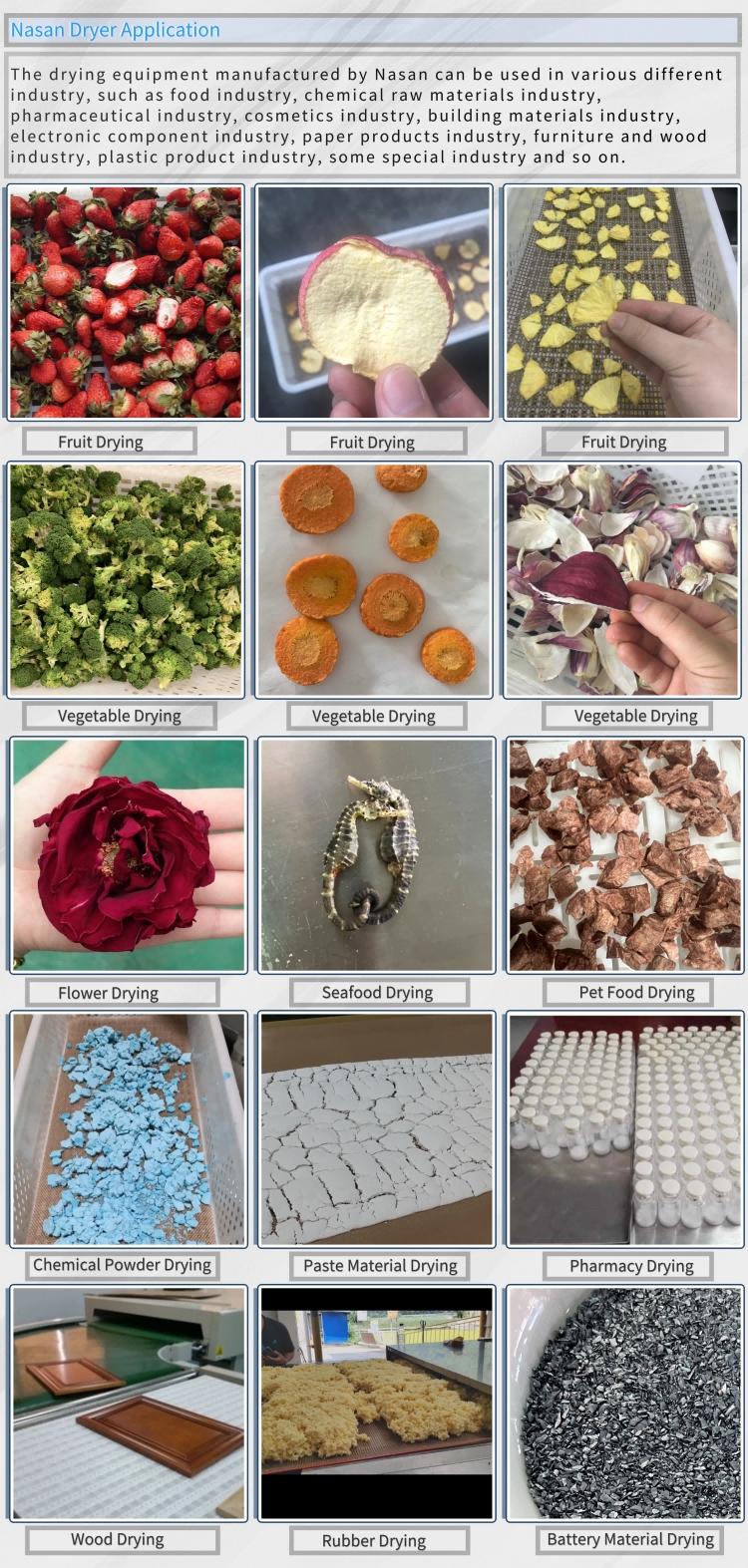
Fruit Dryer
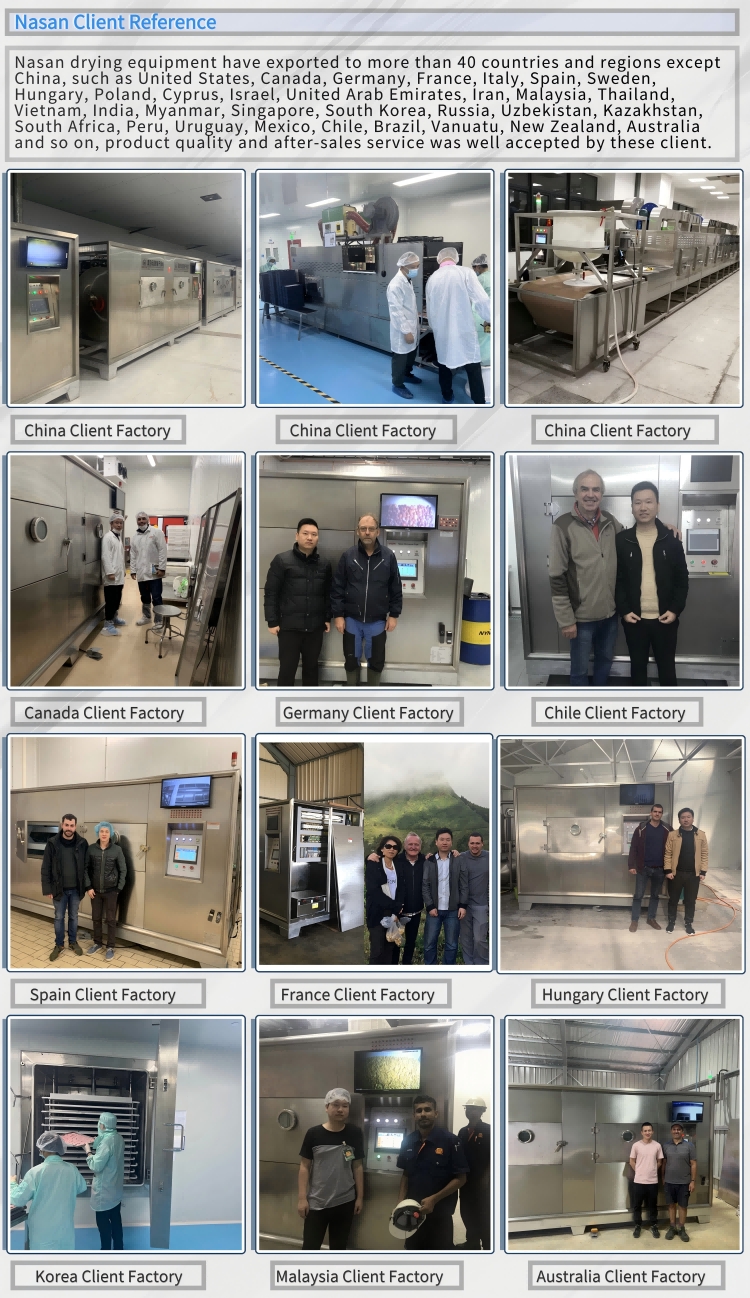
- Nasan Fruit Dryer
- Pineapple Dryer
- Apple Dryer
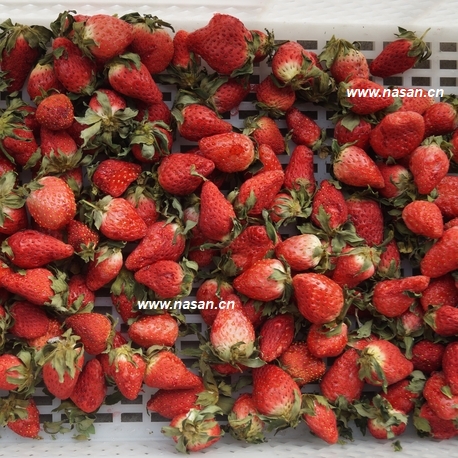
- Strawberry dryer
- Fruit Vacuum Microwave Dryer
- Small Fruit Dehydrator Drying Machine
- Industrial Fruit Drying Machine
- Industrial Fruit Drying Equipment
- Fruit Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Banana Dryer
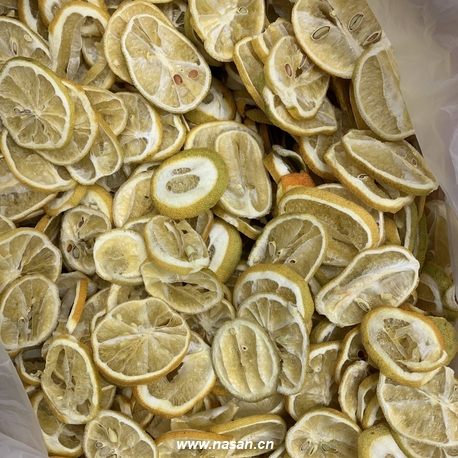
- Lemon Dryer
- Fruit Dehydrator
- Microwave Fruit Dehydrator Machine
- Figs Dryer
- Monk Fruit Dryer
- Kiwi Dryer
- Mango Dryer
- Red Berry Dryer
- Brown Berry Dryer
- Lycium ruthenicum dryer
-
Food Dryer
- Vacuum Food Drying Machine
- Nasan Food Dehydrator
- Mushroom Dryer
- Fish Dryer
- Spring Onion Dryer
- Leek Dryer
- Ginger Dryer
- Yam Dryer
- Beef Jerky Dryer
- Milk Dryer
- Vegetables Dryer
- Chicken Dryer
- Sea Horse Dryer
- Honey Dryer
- Pet food dryer
- Spices Dryer and Sterilize
- Prawn Shrimp Dryer
- Grain Food Dryer
- Chilli Dryer
- Non-fried instant noodles Dryer
- Flower Dryer
- Chemical Dryer
- Material Dryer
- Pharmacy Dryer
- Vacuum Dryer
- Lab Scale Dryer
- Other Dryer