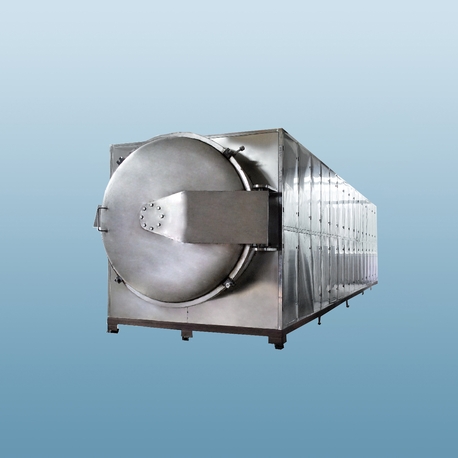
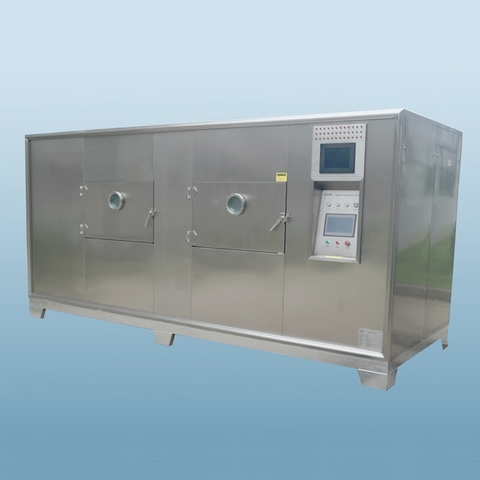
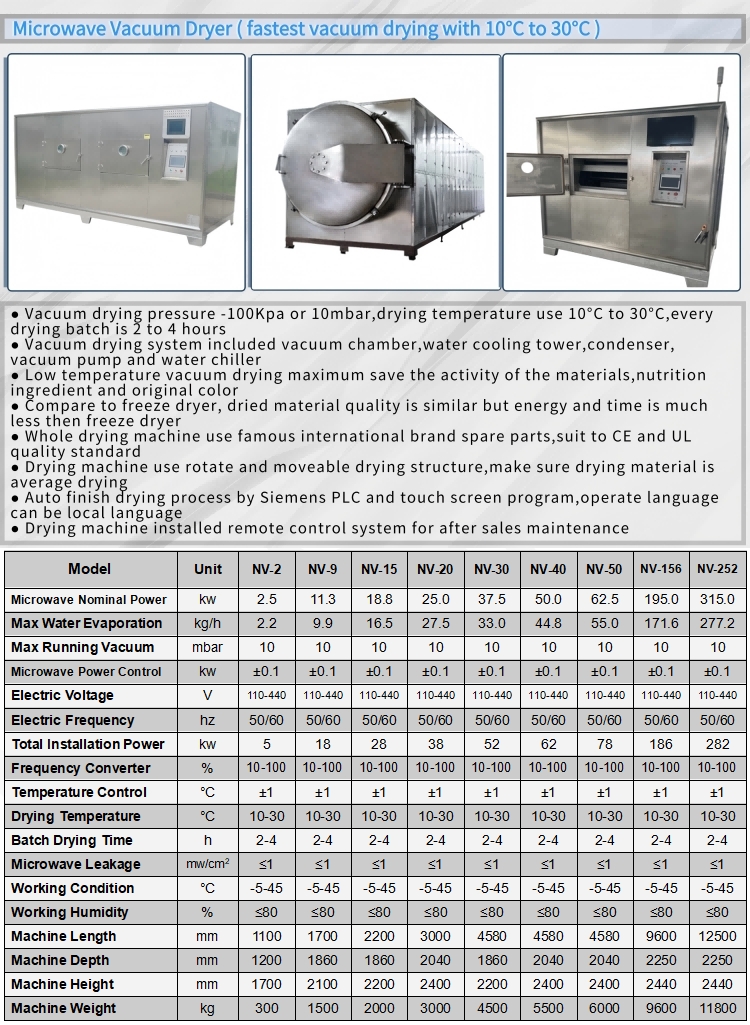
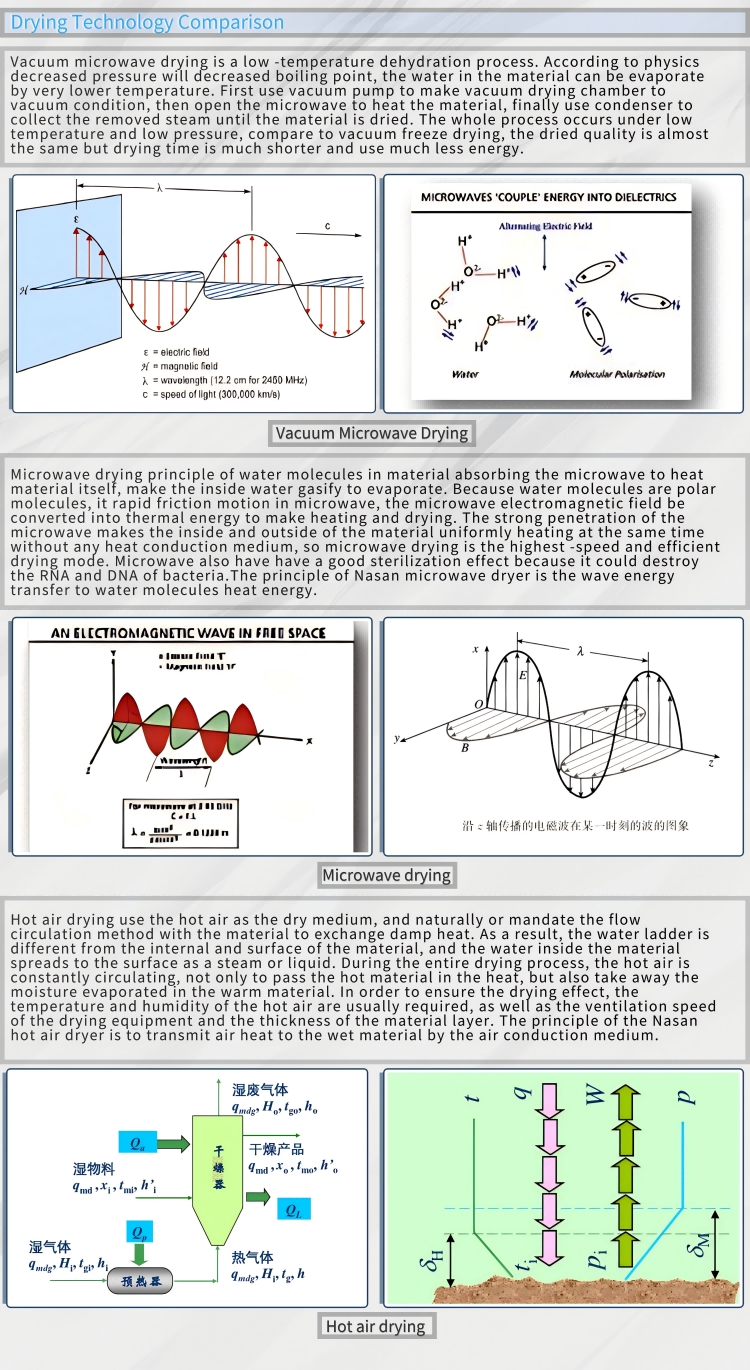
Vacuum microwave dryer (VMD) is an advanced hybrid drying technology that combines the advantages of vacuum drying and microwave drying. It achieves internal heating by penetrating materials through microwave radiation, and at the same time reduces the boiling point under vacuum conditions to accelerate water evaporation. Microwaves use electromagnetic waves to directly act on material molecules to achieve rapid and uniform heating. The drying temperature (10-30°C) is reduced by vacuuming to avoid the denaturation of heat-sensitive materials (such as Chinese medicinal materials, fruits and vegetables) due to high temperature. The combination of microwave and vacuum can shorten the drying time, reduce energy consumption, and retain the color, nutrition and active ingredients of the material.
High efficiency and energy saving: The drying speed is 10-20 times faster than traditional methods, and energy consumption is reduced by 30%-50%.
Low temperature shelf life: The drying temperature is 10-30°C, which is suitable for heat-sensitive materials (such as vegetables, fruits, tea, Chinese herbal medicine, freeze-dried food) to avoid the loss of effective ingredients caused by high temperature.
Uniform drying: Microwaves penetrate the inside of the material, heat evenly, the heating time is short, and the finished product has good rehydration.
Versatility: It can realize integrated operation of drying, sterilization and concentration, and is suitable for pharmaceuticals, food, agriculture, industrial raw materials and other fields.
Advantages of VMD (Compared to Traditional Drying)
Vacuum microwave dryer outperforms traditional drying methods (hot air drying, vacuum freeze drying) in multiple dimensions, making it suitable for high-value, heat-sensitive materials. The comparison below highlights its core strengths.
Use fruit as a comparison sample as below:
| Fruit vacuum microwave dry | Fruit vacuum freeze dry | Fruit Hot air dry |
| Drying Temperature | 10 ~ 30°C | -40 ~ 30°C | 60 ~ 85°C |
| Drying Time | 2~4h | 24~120h | 12-72h |
| Energy consumption | low | very high | very low |
| Sterilized | yes | no | no |
| Nutrient | High (retain 80–90% vitamin C,
90%+ dietary fiber/antioxidants) | Very high (retain 90–95%,
but high costly) | low (retain 30–50% vitamin C,
most lost to heat with oxygen) |
| Shape | 90% of original | 100% of original | 50% of original |
| Color | Bright, true to fresh | White,near fresh | Darkened (browning) |
| Flavor | Intense, no “cooked” taste | Intense (but 2–3x more expensive) | Weak, “stale” |
| Texture | Chewy or crispy (controllable) | Puffy, crispy | Hard surface, dry interior |
| Eat feeling | delicious | boring | normal |
| Contamination Risk | Low (closed system, no dust/insect contact) | Low (closed system,no dust/insect contact) | Medium (open air may carry impurities) |
| Machine cost | middle | very high | lower |
Additional advantages:
No surface hardening: Since heat is generated internally, moisture evaporates from the inside out, avoiding the "crust" formed by surface drying in traditional methods (critical for porous materials like fruits and vegetables).
Sterilization effect: Microwaves have a certain bactericidal effect (destroying microbial cell membranes), which can extend the shelf life of dried products.
Flexible control: Drying parameters (microwave power, vacuum degree, temperature) can be adjusted in real time to adapt to different materials.
Applications of VMD
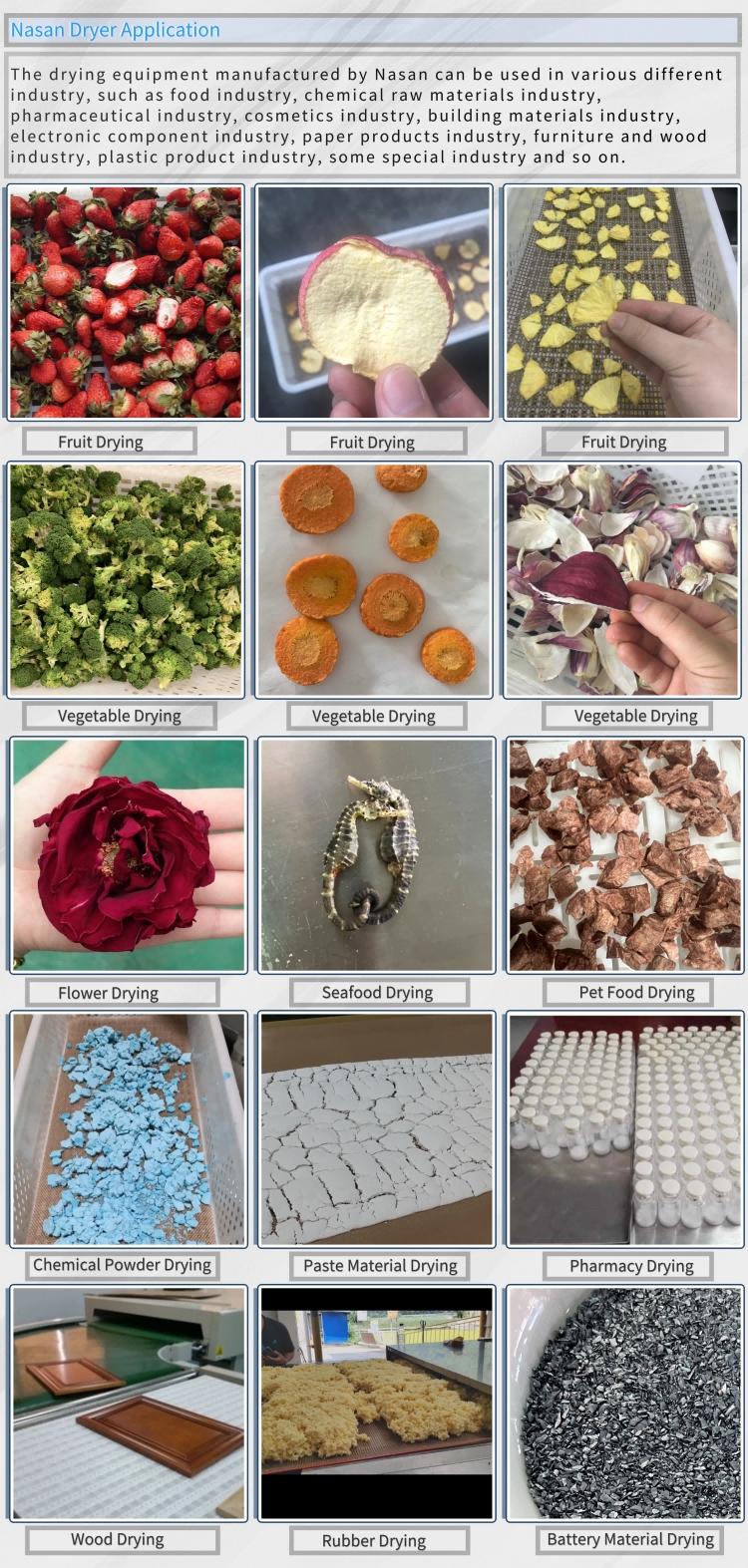
VMD is widely used in industries requiring high-quality, low-temperature drying, especially for heat-sensitive, high-value materials. Key application areas include:
(1) Food Processing Industry
Fruits and vegetables: Drying of strawberries, mangoes, mushrooms, and garlic. For example, VMD-dried strawberries retain more anthocyanins (antioxidants) and have a better rehydration rate (can quickly absorb water to restore texture) compared to hot air-dried ones.
Herbal products: Drying of ginseng, astragalus, and chrysanthemums. The low-temperature environment preserves heat-sensitive active ingredients (e.g., ginsenosides in ginseng) that would be destroyed by high temperatures.
Seafood: Drying of shrimp, scallops, and fish. VMD avoids the "fishy smell" caused by high-temperature oxidation and maintains the tenderness of seafood.
(2) Pharmaceutical Industry
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs): Drying of heat-sensitive drugs (e.g., antibiotics, enzymes). VMD ensures the stability of APIs and avoids degradation.
Herbal extracts: Concentration and drying of liquid extracts (e.g., traditional Chinese medicine extracts). It prevents the loss of volatile components and improves product purity.
(3) Agricultural and Biological Fields
Seed drying: Drying of crop seeds (e.g., rice, corn) at low temperatures to maintain germination rate (high temperatures in traditional drying easily kill seed embryos).
Biological samples: Drying of microorganisms (e.g., yeast) and biological tissues (e.g., animal cells) for preservation.
In summary
vacuum microwave drying is a high-efficiency, high-quality drying technology that is particularly suitable for heat-sensitive, high-value materials. With the advancement of equipment and process optimization, it will play an increasingly important role in food, pharmaceutical, and biological industries.